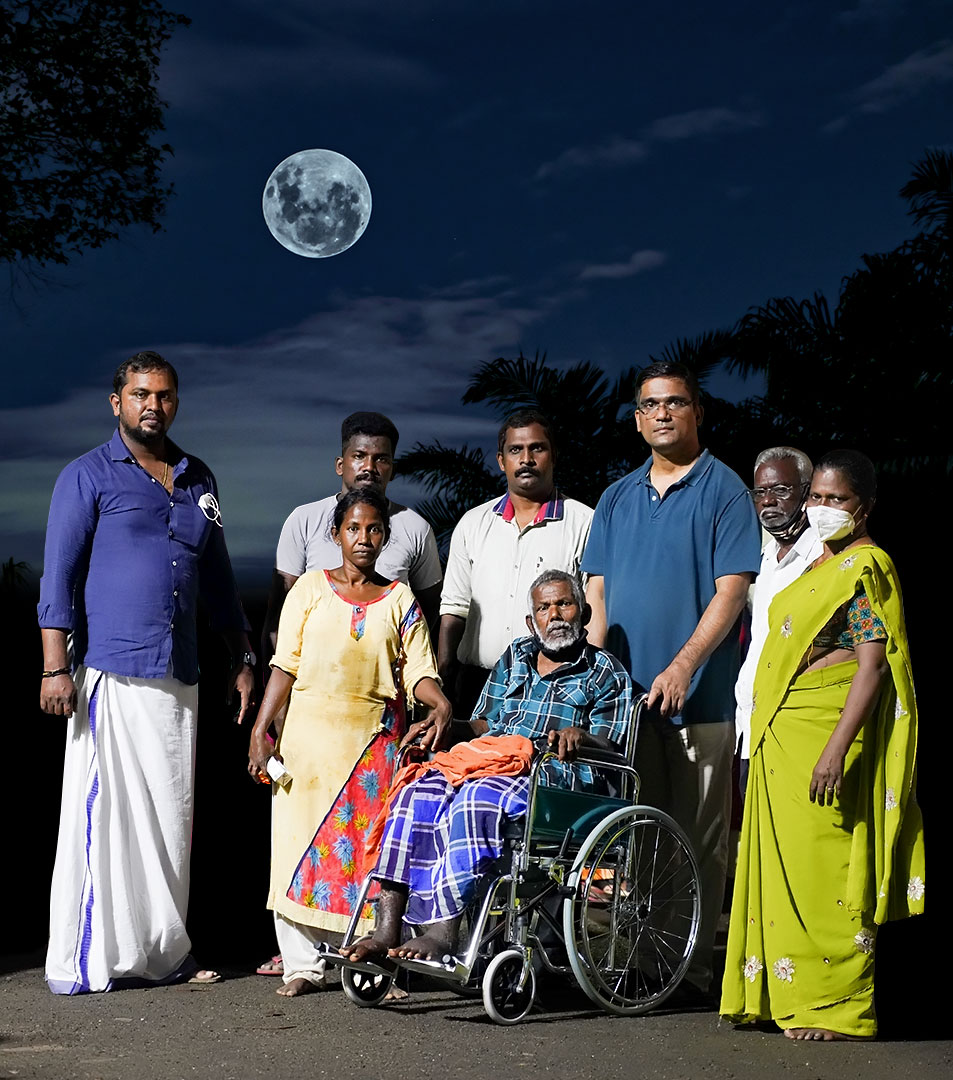
Success stories
Stories that vouch
I am Preetha. I come from Karimadom, an urban colony in Trivandrum. I grew up in a community isolated from mainstream society, with zero possibility for a bright future. From the 5th standard, my life took an unexpected turn. Don Bosco Veedu implemented a project to educate the children in our colony. As a result, I got scholarships from Don Bosco, which has significantly impacted my academic life. Don Bosco took us for picnics, conducted summer camps, and gave us Christmas gifts. All these gave me new exposure and built my self-confidence. With their support, I graduated from Mar Ivanios College with a B.Com degree. In addition, I was also able to develop my computer skills during this period. Later I joined and volunteered in the tuition...